Institute for power electronics and control of drives
Alexander Sauer M.Sc.

Institute for power electronics and control of drives

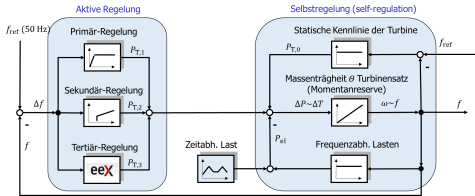
The transformation of the electrical power supply in Germany, which is commonly referred to as energy conversion, is characterized by the transition of a system with central generation within large power plant units with approx. 1 GVA electrical power to a System in which the generator units are arranged smaller and decentralized. These small and medium-sized generation units (wind, photovoltaic, CHP) and storage of subscriber lines in the area up to 10 MVA are almost exclusively connected by power electronic systems (inverters, especially “Active Infeed Converter”, shortly AIC) to the medium- and low-voltage network.
In this project mainly technical questions are addressed. These questions mainly arise from the fact that the stability and the quality of the supply is not determined by the intrinsic behavior of large machine sets (overload capacity, mass inertia), but by the behavior implemented in the inverter in the case of a large number of decentralized generating units connected via inverters. As a limiting case, one can start from the idea that the grid is fed exclusively by inverter-coupled generators.
The overall objective of the project is to develop and test methods for the stable operation of a power supply network in a multitude of decentralized consumers connected via inverters to ensure a high supply quality and reliability.
Scientific work
We would like to customise the information and usability of this website to your preferences and needs.
To this end, we use so-called cookies. Please choose which cookies you would like to enable when visiting our webpages.
Some of these cookies are required to load and correctly display this website on your device.
These are strictly necessary or essential cookies and cannot be deselected.
The preferences cookie saves your language setting, while the statistics cookie regulates
how the open-source statistical software “Matomo” analyses your visits to and activities on our website.
For more information about cookies we use, please refer to our
privacy policy.